Blog entry by Admin User
Anyone in the world


Practice title:
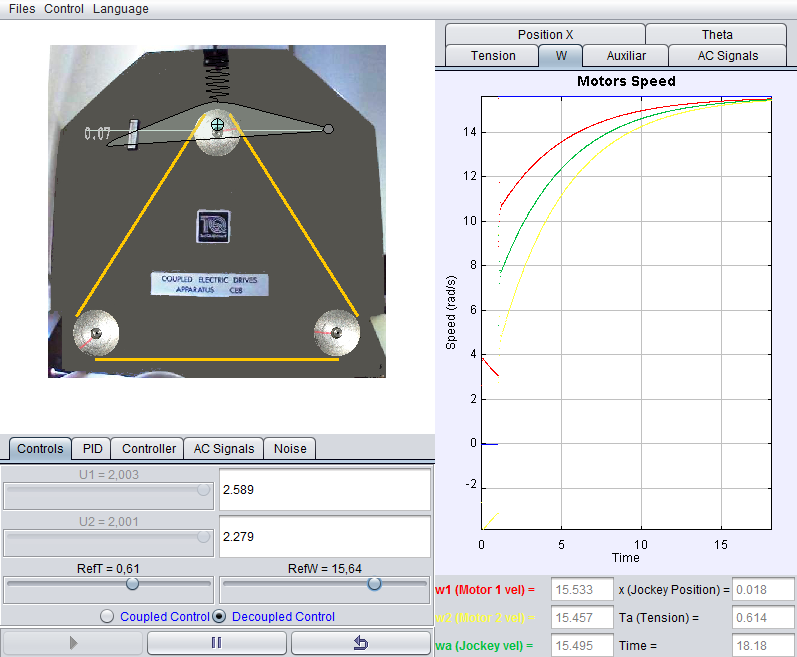
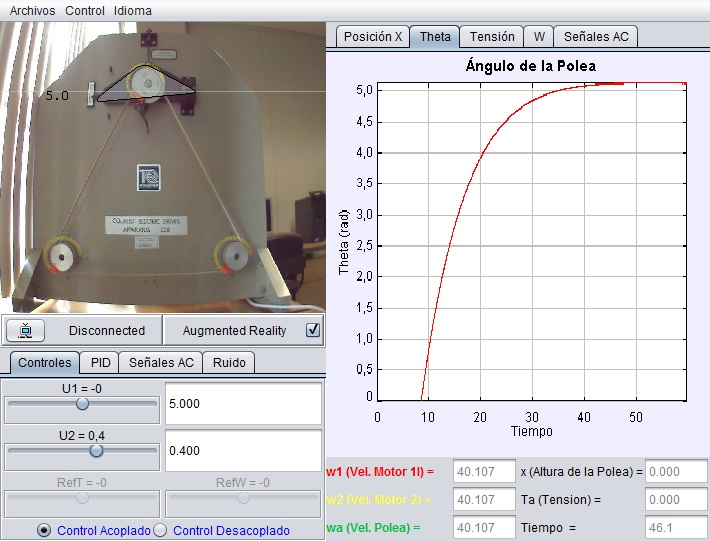
Tension and velocity control of a belt on a two coupled electric drives system
The device has two electric drives, coupled by means of a flexible belt. The belt passes through a pulley with a system that allows measuring its velocity and tension. The main control problem is to change the torque in the two motors in order to regulate the tension and the velocity of the belt. This can be done either individually or simultaneously. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Independent control of the velocity and tension of the belt.
- Simultaneous control of the velocity and tension of the belt.
- Practical methods for the multivariable control of electromechanical systems.

Practice title:
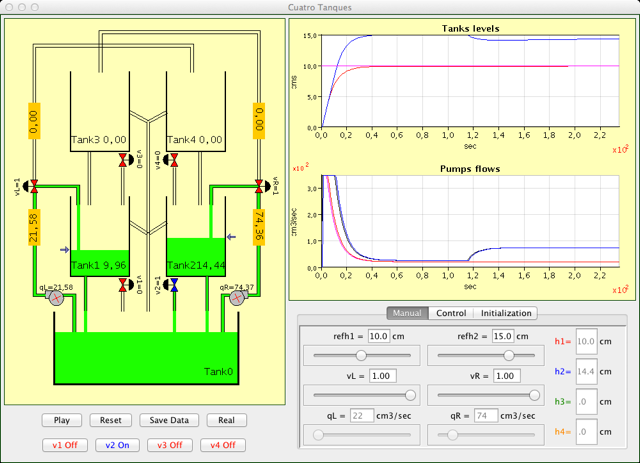
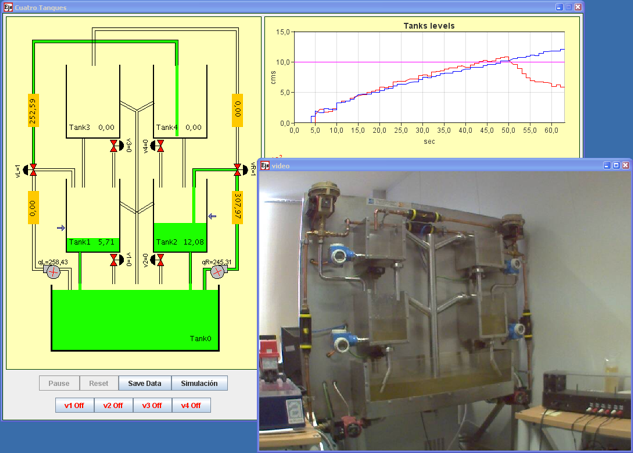
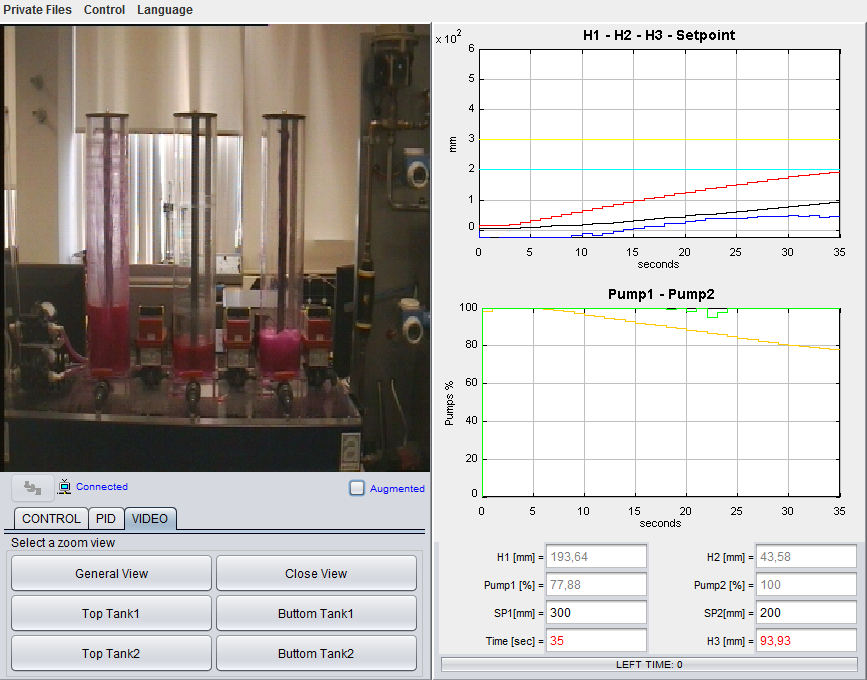
Level control in a four tanks system
The system of four tanks is one of the most used in the learning of multivariable process control. The system is composed by four tanks. At the bottom of each of them there is an outlet of known section and another one with an unknown section, regulated by means of a valve that enables or disables the corresponding perturbation. The system also has two three-way valves that allow regulating the flow, coming from two pumps, that enters in each one of the tanks. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study of the dynamic characteristics of the system.
- Modeling of the system by means identification techniques.
- Design of a multivariable controller to regulate the level of one tank.

Practice title:
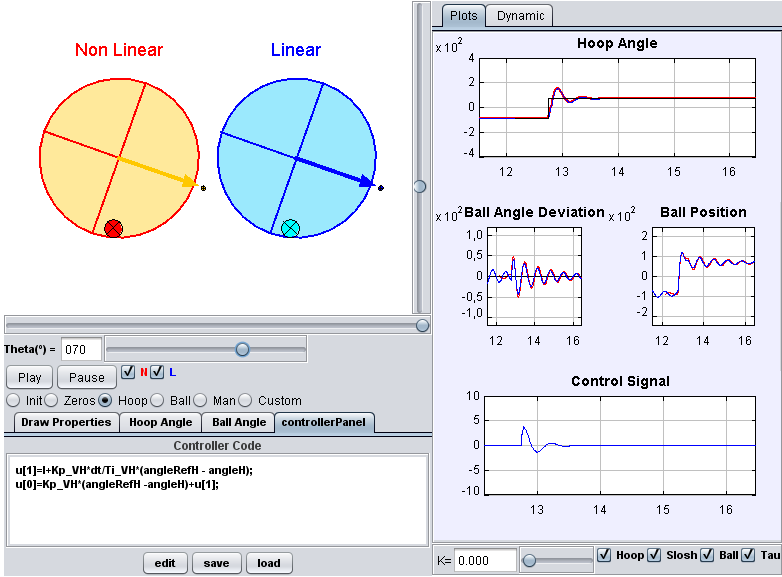
Control of the ball and hoop system
The Ball and Hoop system is an electromechanical device consisting of a ball rolling on the rim of a hoop. The hoop is mounted on the shaft of a servomotor and can rotate about its axis. The rotation of the hoop causes an oscillatory movement of the ball around its equilibrium point. The behavior of the ball is similar to the dynamic of a liquid inside a cylindrical container. The main objective of this system is to control these oscillations. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study the transmission zeroes and non-minimum phase behaviors.
- Velocity and position control of the hoop.
- Control of deviation of the ball from its rest position.


Practice title:
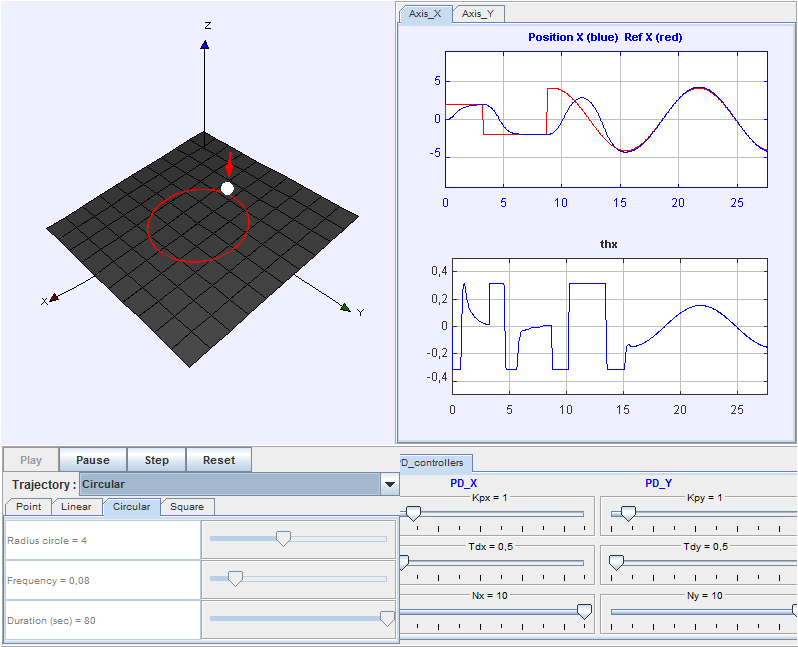
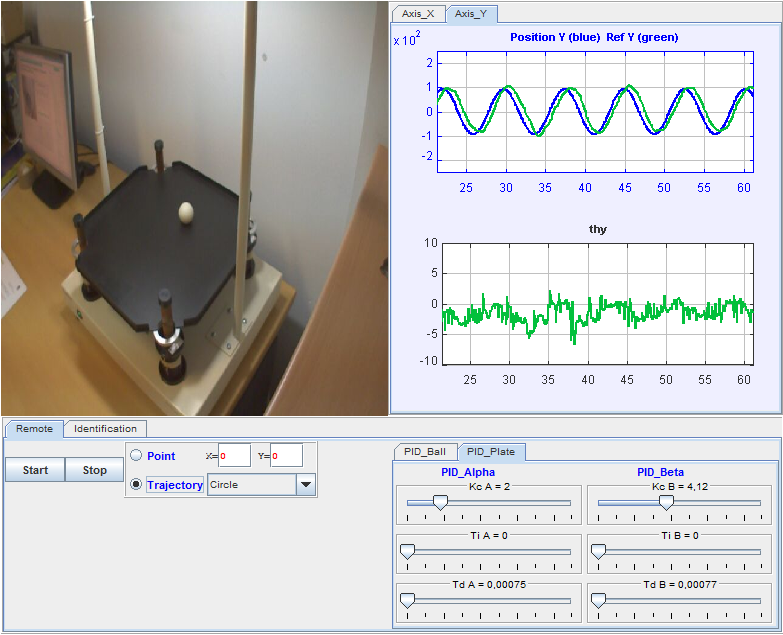
Control of the ball and plate system
The Ball and Plate system is an electromechanical device consisting of a ball rolling on a rigid square plate. The main purpose of this system is to control the position of the ball by manipulating the slope of the plate in two perpendicular directions. This system is considered to be a bidimensional extension of the traditional ball and beam system and it is emplyed in the aeronautical industry for the development of aerial and terrestrial vehicles simulators. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Position control of the ball in a point.
- Trajectory tracking of the ball.

Practice title:
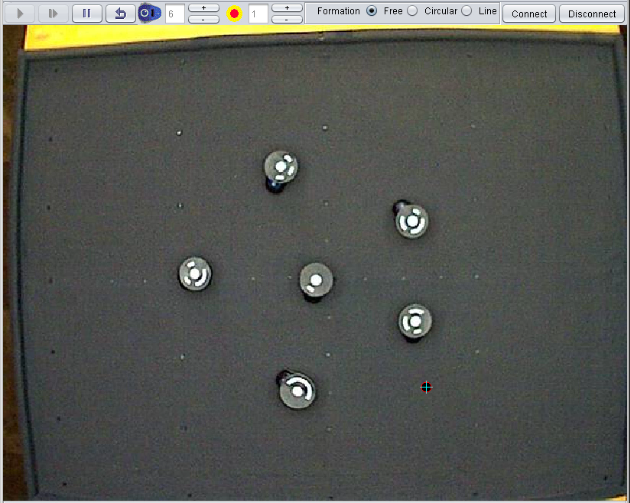
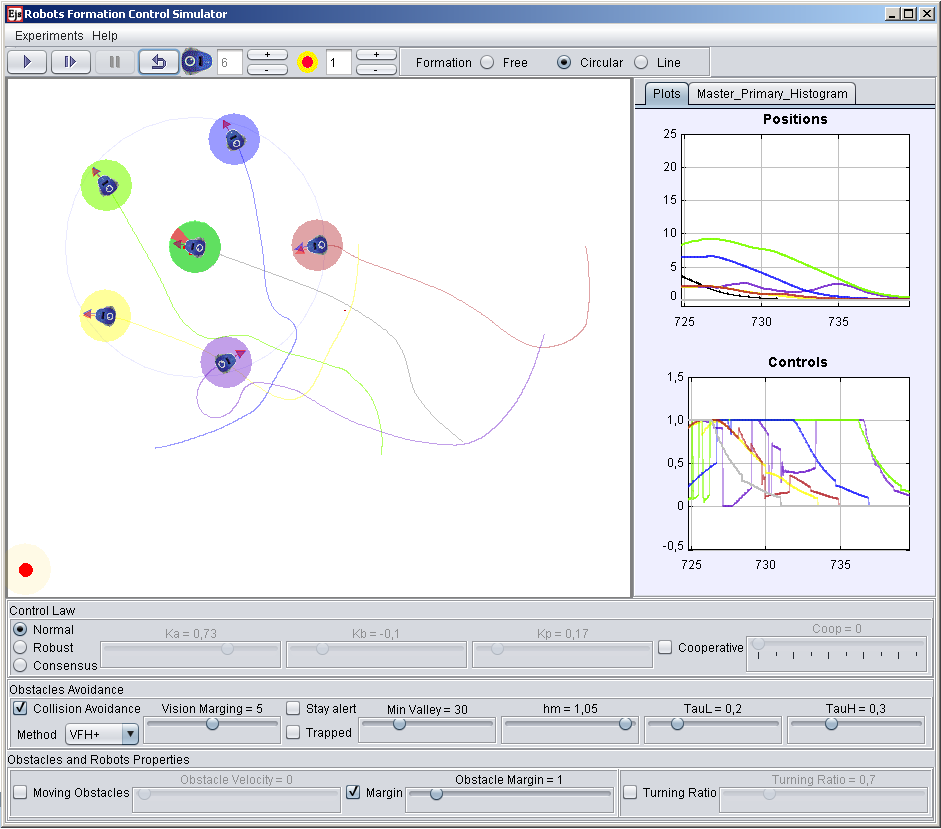
Mobile robots control (multi-agents system)
This laboratory is based on a multi-agents system consisting on a group of small wheeled robots (Moway). These robots are composed by five modules: processing system, drive system, sensors and indicators group, power supply system and the expansion connector for radiofrequency wireless communication (RF). The robots can communicate with each other, avoid obstacles and cooperate in a master-slaves architecture. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Position (point stabilization) controlling of mobile wheeled robots.
- Implementing obstacles avoidance algorithms.
- Formation controlling of a multi-agents system with obstacles avoidance.


Practice title:
Control of the ball and beam system
The system consists of two different subsystems: the ball and beam itself and a motor with a gear wheel, which is connected to the first module through a level arm. The beam consists of a steel rod in parallel with a nickel-chromium wire-wound resistor forming the track on which the ball is free to roll. Measuring the voltage in the steel rod provides the position of the ball in the beam. The control objective of this system is to move the ball to the desired position in the beam. For this purpose, two measurements are taken (the position of the ball and the angle of the motor), and the control signal is applied to the motor. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study of the dynamics of the system.
- Study and the design of a control system for the position of the ball.

Practice title:
Nonlinear control of a Furuta pendulum
The Furuta pendulum is a device consisting of an inverted pendulum pivoting on a rotating base. The turn of this base allows to control the position of the pivot and thus indirectly the angle of the pendulum. This is a challenging device because is unstable (with the pendulum in the upwards position) and it also exhibits non minimum phase behavior. The objective of the practice is to develop a nonlinear control strategy that is divided in two steps:
- Develop a control law that keeps the pendulum on an upwards position while the pivot of the pendulum follows a reference signal. This control law is based on linearization around the unstable equilibrium point.
- Implement a swing up control that is able to lift the pendulum from its stable equilibrium position (downwards) to its unstable equilibrium point (upwards) in order to apply the control developed on the previous step.

Practice title:
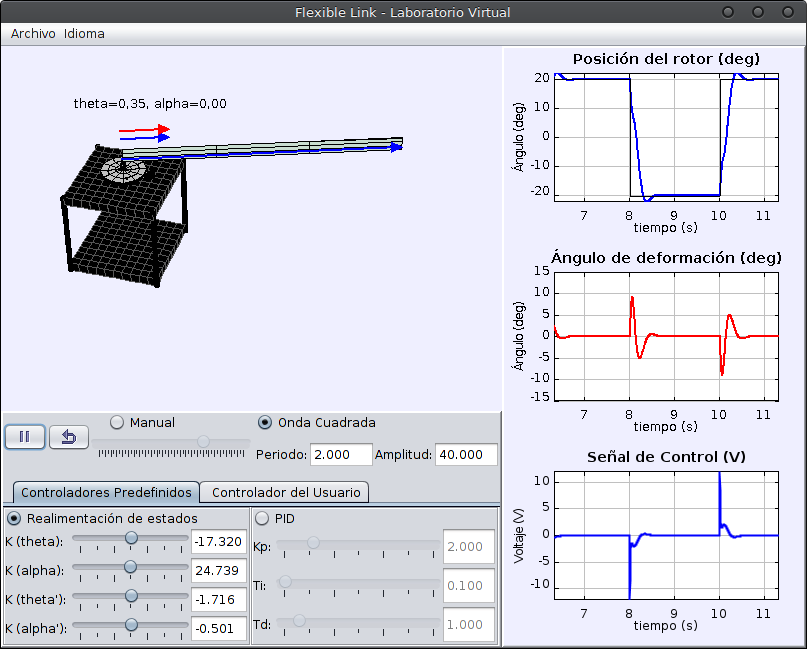
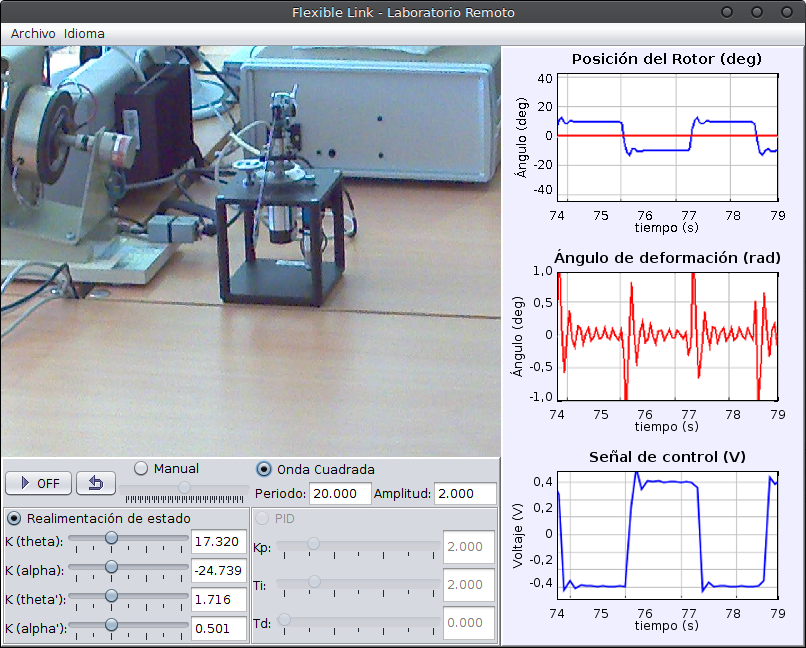
Position and vibration suppression control of a flexible link
The Rotary Flexible Link module consists of a thin stainless steel flexible link with one end free, and a DC motor used to rotate the link from the other end in the horizontal plane. The main control problem is the position control of the tip, supressing or minimizing the vibrations that appear due the the elasticity of the link. The built-in sensors of the module provide the position and velocity of the DC motor, and the deflection of the tip. The control variable is the input voltage of the motor. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Position control with a PID controller.
- Position control with a state-feedback controller and LQR control.

Practice title:
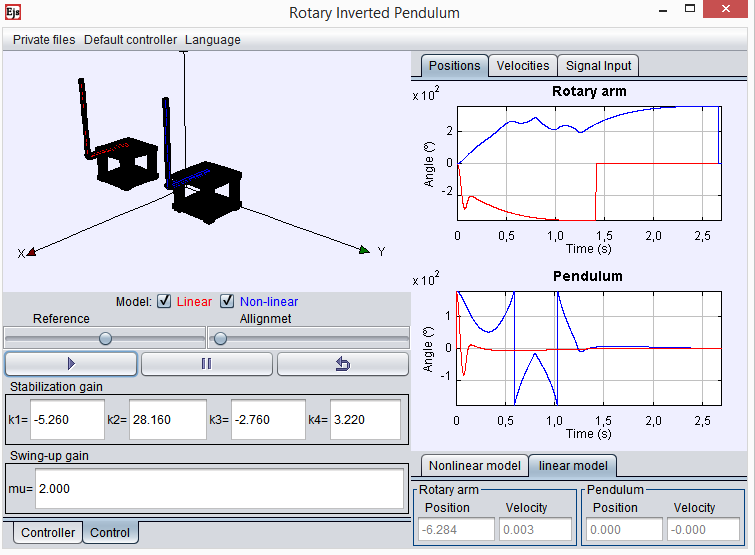
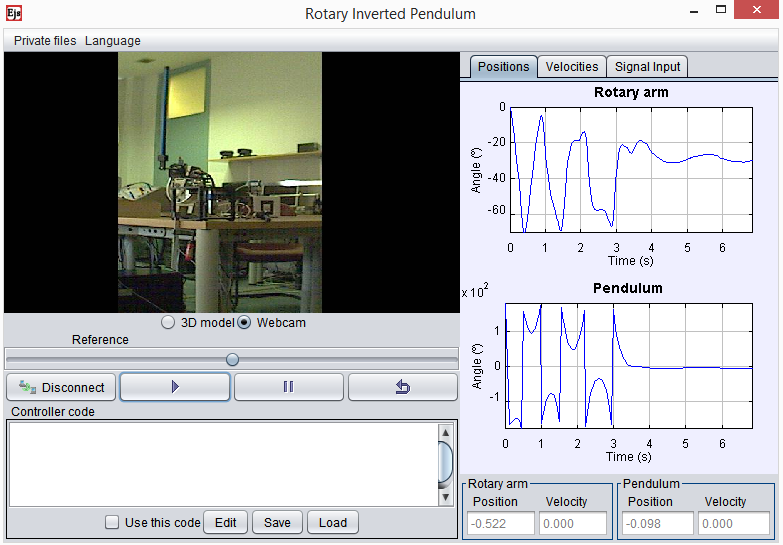
Control of an inverted pendulum
The rotary inverted pendulum consists of a motor which has a rotary arm attached that can move free 360º. The pendulum is connected at the end of the rotary arm and it can oscillate freely and perpendicularly to the rotary arm. The main characteristics that make it an interesting case of study are that it is a strongly nonlinear, unstable, non minimum-phase, and underactuated system. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Nonlinear control to swing-up the pendulum from the stable equilibrium point to the unstable equilibrium point.
- Linear control to stabilize the pendulum in the unstable equilibrium point.

Practice title:
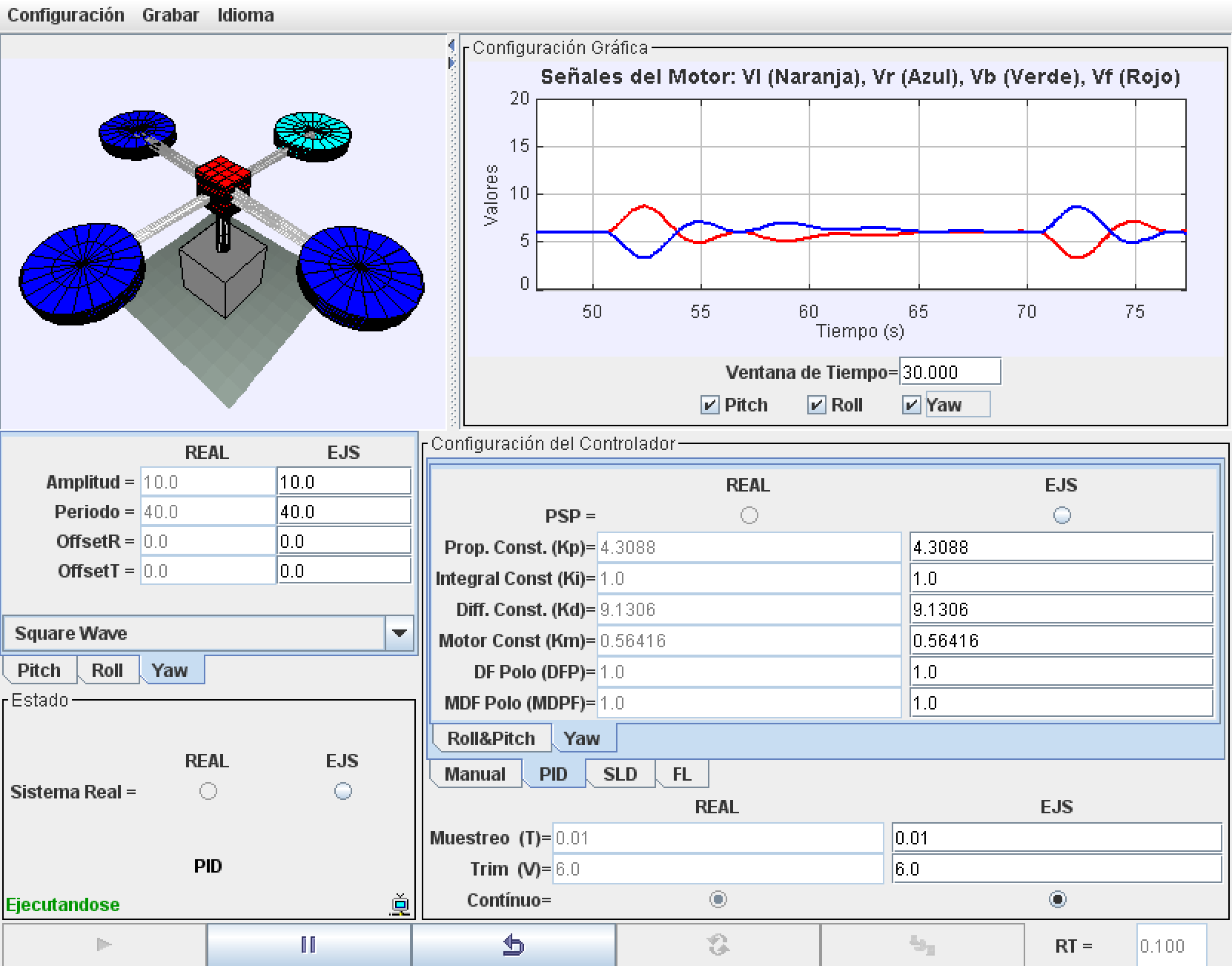
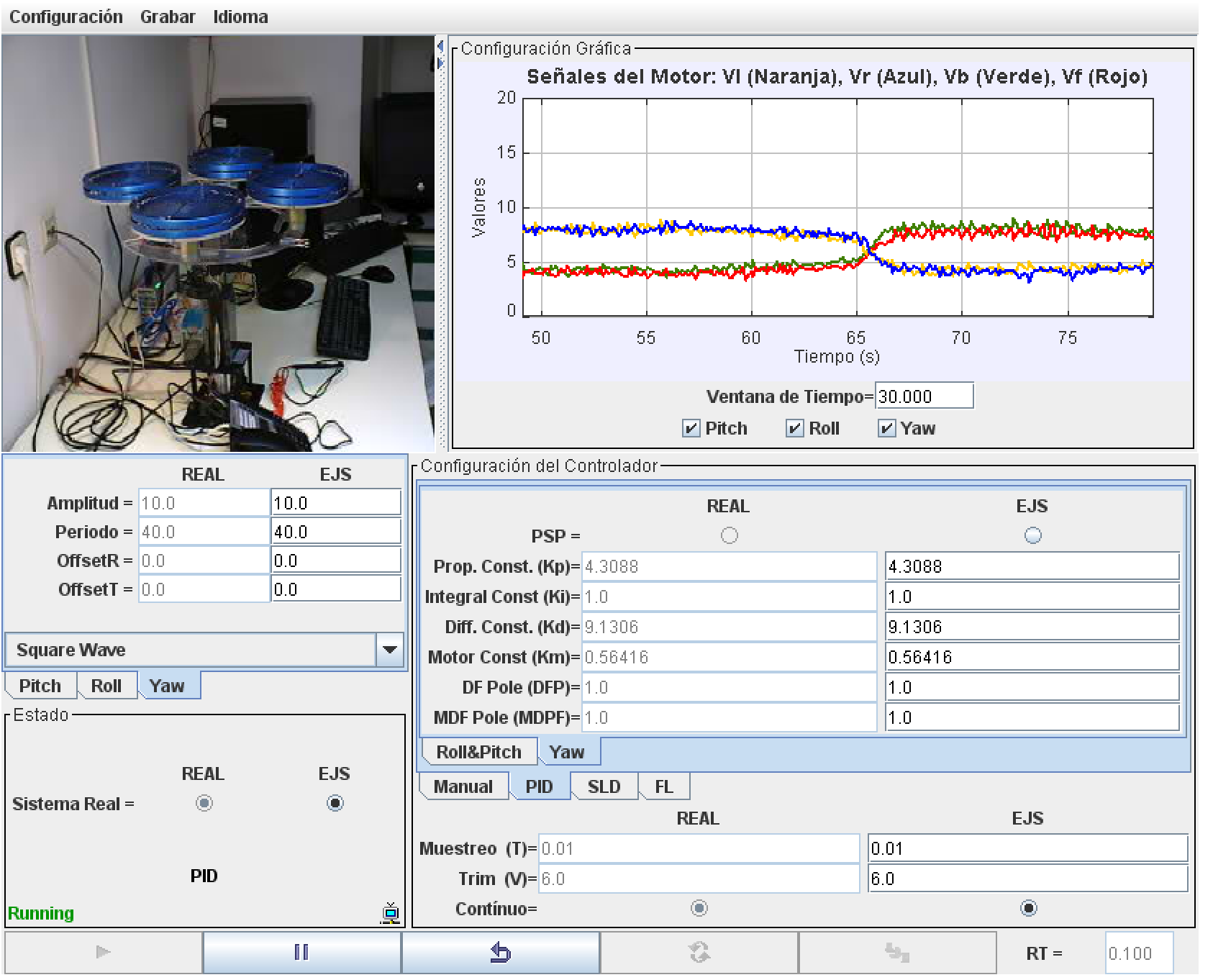
Controlling a 3 DOF Quadrotor
This plant is a non-linear system consisting of a frame with 4 propellers mounted on a 3 DOF pivot joint. The joint permits the frame to freely roll, pitch and yaw, due to the lift force and the torque generated by the propellers, each coupled to a DC motor. The maximum pitch and roll are limited to +-40º. The power applied to each motor is used to independently control the angular speed of each propeller. The orientation of the frame is determined by the optical encoders mounted over each axis. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- System Identification.
- Linear control design: PID, state feedback controller.
- Non linear control design: feedback linalization and sliding controller.

Practice title:
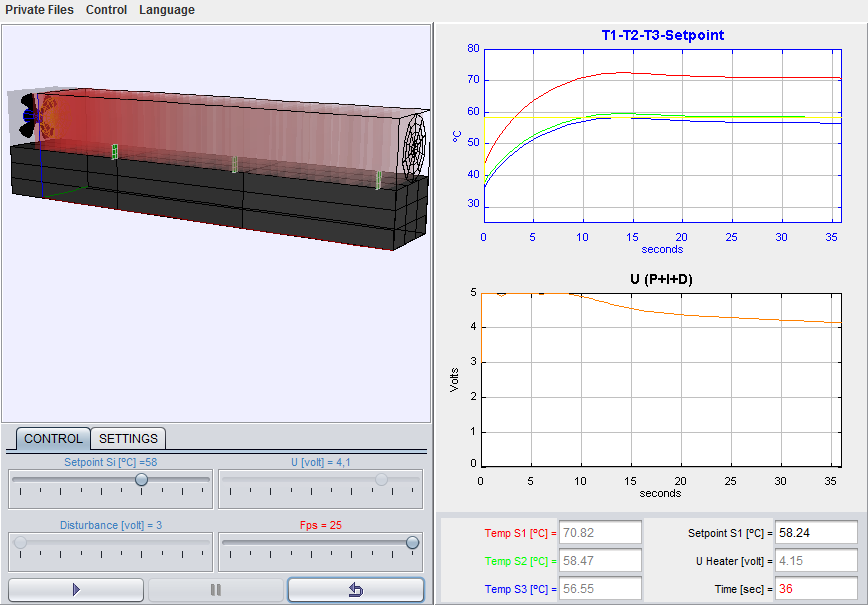
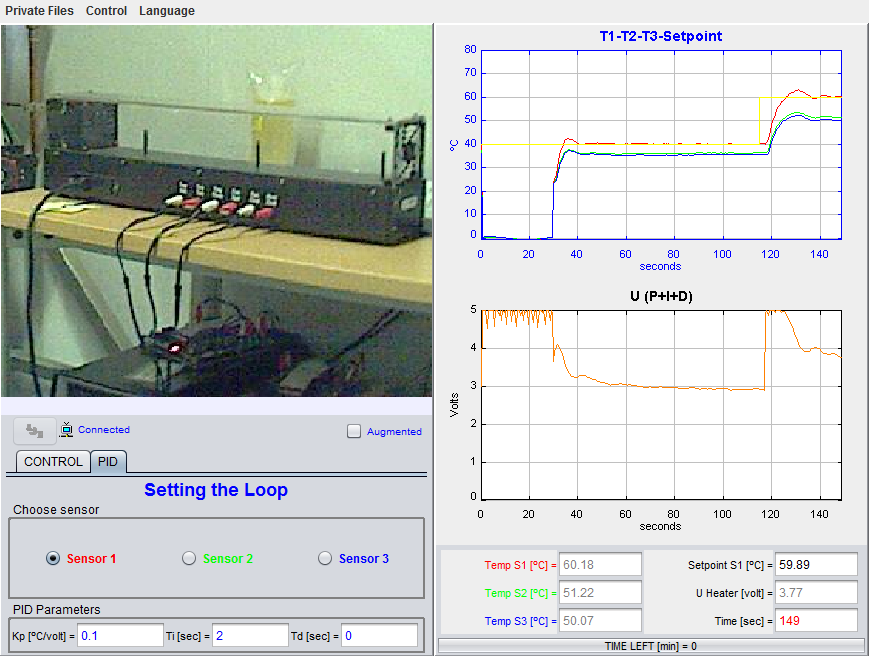
Temperature control in a heat exchanger system
This device consists on a box equipped with the following components: a heater and a fan placed in one of the extremes of the device and three temperature sensores placed in different points along the box. The power for the heater and the fan velocity are controlled using analogic signals. Temperatures are measured using platinum transductors due to their velocity in the stabilization of the measurements. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study of the system's static and dynamic properties.
- Analysis and experimentation with a PI temperature control.
- Study of the effect of perturbation over the real system.
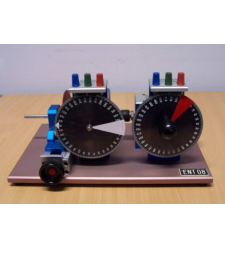
Practice title:
Position and velocity control with a direct current motor
This system is a DC motor with a rev counter. The motor moves a load which consists in a steel disc. An adjustable magnetic break applies a viscous friction effect, allowing therefore the modification of the time constant of this first order system. The angular position and velocity of the motor are controlled adjusting the input voltage. The position is measured with a potentiometer connected to the axis of the motor. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study of the system's static and dynamic properties.
- Study and design of a control system in velocity.
- Study and design of a control system in position.
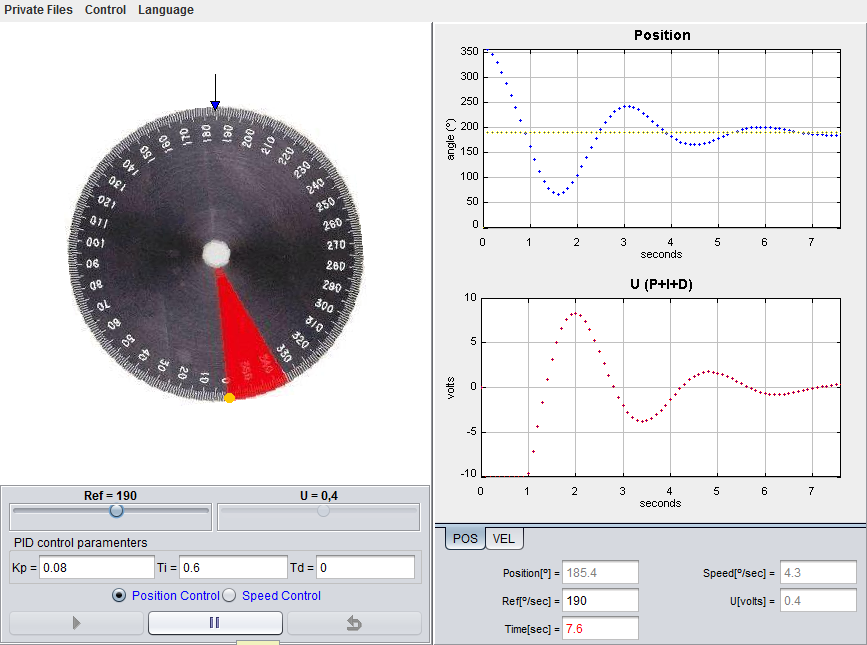
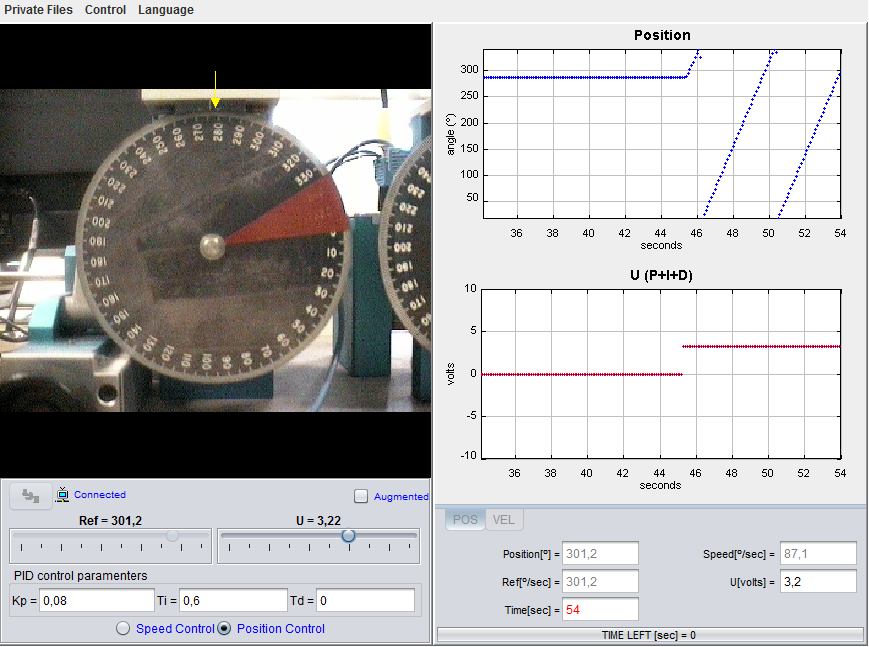

Practice title:
Liquid level control in a three tanks system
This plant has three cylindrical deposits or tanks. The three tanks are connected between them in series and they count with their own unloading pipes. The liquid that leaves the tanks is collected in a big rectangular deposit placed at the bottom of these tanks. This same deposit serves as the source for the pumps that inject liquid to the tanks placed on the extremes. With this laboratory you can perform, among others, these tasks and activities:
- Study of the system's dynamic properties.
- Analysis and experimentation for a liquid level control.
- Study of the effect of perturbation over the system.
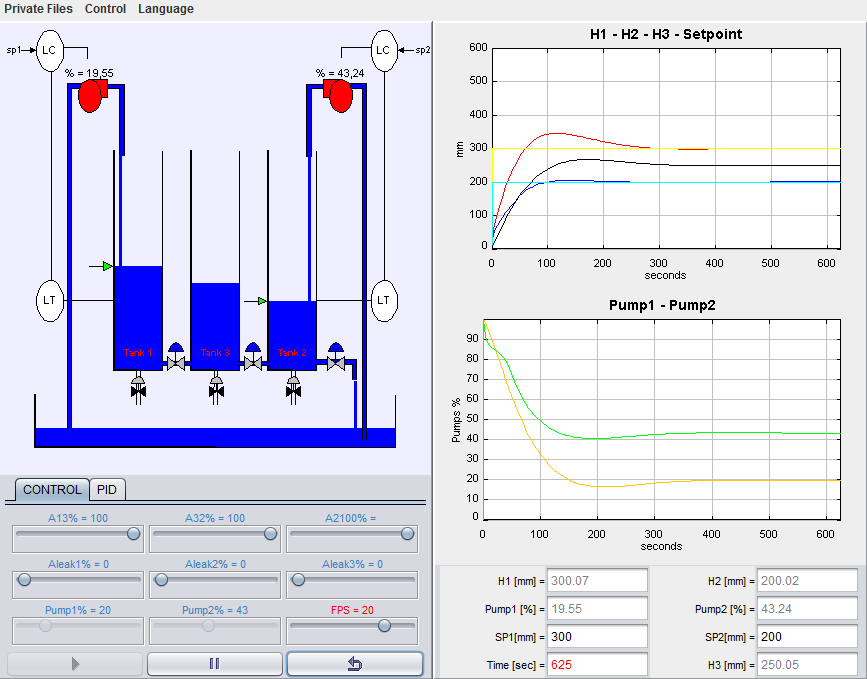

Practice title:
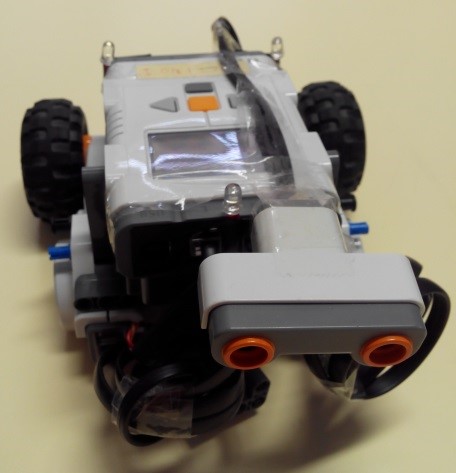
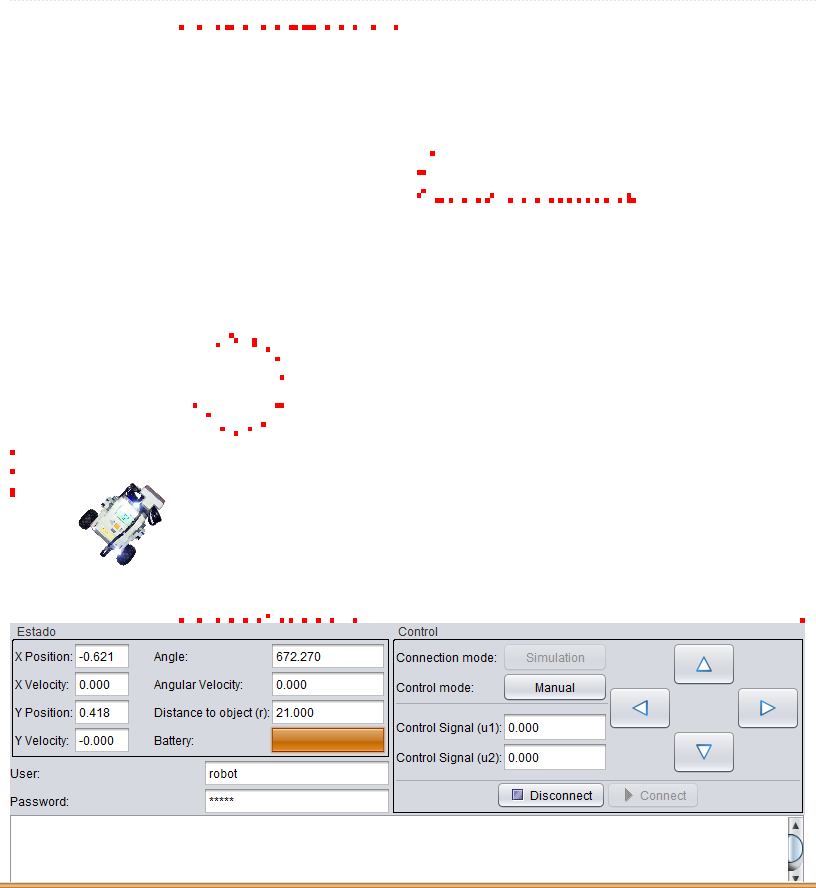
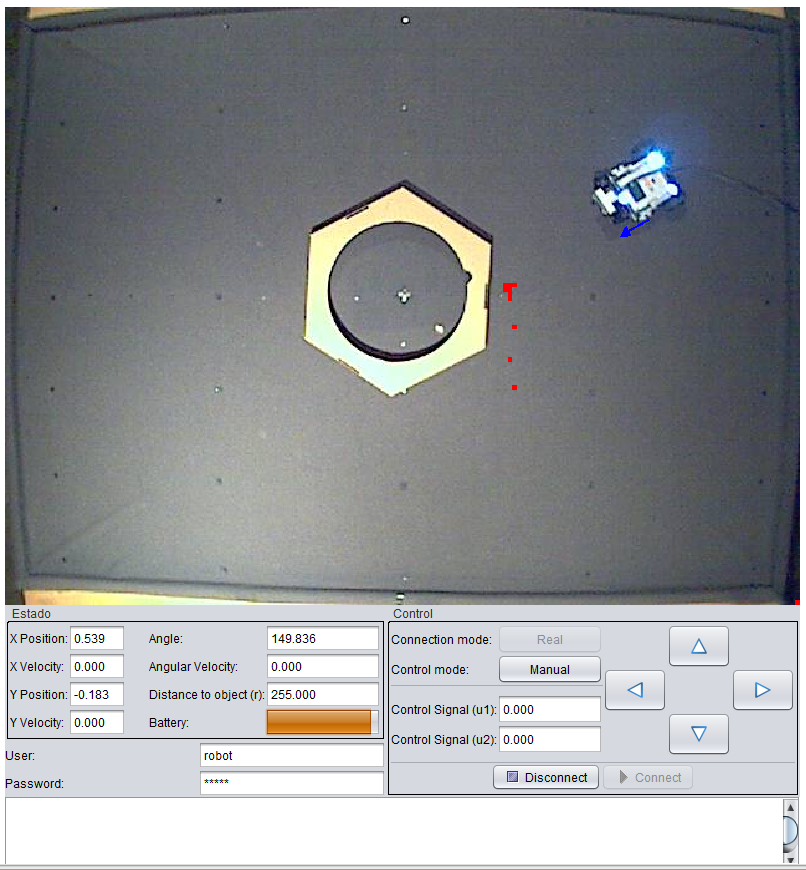
Control of an autonomous robot
In this practice, an autonomous underactuated mobile robot equipped with differential wheels is controlled. The objective is to locate the obstacles that are present in its playground in order to draw a map. In particular, you can perform, two different tasks and activities with this laboratory:
- Creation of maps: In this task the student must develop a map of the robot environment based on the measurements of the external sensors and the absolute position measurement obtained from an artificial vision system external to the robot.
- Position Control: In this second task a position control algorithm will be implemented by the student. This algorithm must take into consideration the map previously created on the first task to plan the trajectory as well as the measurements or the sensors in order to avoid collisions.
More coming soon...
You want to add your own remote lab to our network? Visit our remote lab repository and do it with just a few clicks!
[ Modified: Thursday, 15 October 2015, 11:59 AM ]
